Blood collection tubes are an essential tool in laboratory diagnostics, used for drawing, storing, and transporting blood samples for various tests. Whether you are a healthcare professional, researcher, or someone interested in understanding more about the process, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know about blood collection tubes.
What Are Blood Collection Tubes?
Blood collection tubes are sterile vacuum sealed container used to collect and store blood samples for medical testing. They come in various sizes and are made of different materials, depending on the type of test being performed. The tubes are typically sealed with rubber stoppers and can contain various additives like anticoagulants, clot activators or preservatives.
These tubes are primarily used for laboratory tests such as blood chemistry, hematology, serology, and microbiology. The type of tube used depends on the specific requirements of the test.
Types of Blood Collection Tubes:
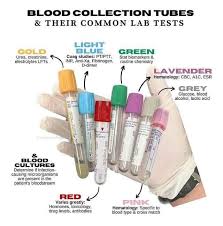
Blood collection tubes are color-coded to signify the type of additive inside. Here’s an overview of the most common types:
1. Red Top Tube (No Additive)
- Use: For serum collection.
- Common Tests: Serum chemistry, hormone testing, and serology.
- Description: These tubes contain no additives, allowing the blood to clot naturally. After clotting, the serum can be separated from the blood cells by centrifugation.
2. Blue Top Tube (Citrate)
- Use: For coagulation studies.
- Common Tests: Prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT).
- Description: Contains sodium citrate, an anticoagulant that binds calcium to prevent clotting. Used for tests that evaluate blood clotting.
3. Green Top Tube (Heparin)
- Use: For plasma collection.
- Common Tests: Blood gas analysis, electrolyte testing, and toxicology.
- Description: Contains heparin, which is a powerful anticoagulant that prevents clotting by inhibiting thrombin.
4. Lavender Top Tube (EDTA)
- Use: For hematology tests.
- Common Tests: Complete blood count (CBC), blood typing, and hemoglobin levels.
- Description: Contains EDTA, which prevents blood from clotting by binding calcium. This tube is ideal for hematology and blood typing tests.
5. Yellow Top Tube (ACD or SPS)
- Use: For blood culture and DNA studies.
- Common Tests: Blood cultures, DNA testing.
- Description: Contains either acid-citrate-dextrose (ACD) or sodium polyanethol sulfonate (SPS) to prevent clotting and preserve DNA. Often used in microbiology and genetic testing.
6. Gray Top Tube (Oxalate/Fluoride)
- Use: For glucose testing and preservation.
- Common Tests: Glucose tolerance tests, lactate testing.
- Description: Contains sodium fluoride, which inhibits glycolysis, thus preserving glucose levels in the blood sample.
7. Pink Top Tube (EDTA – Blood Bank)
- Use: For blood bank testing.
- Common Tests: Blood crossmatching, antibody screening.
- Description: Contains EDTA, similar to the lavender top, but specifically designed for blood bank purposes. This tube is used to preserve the integrity of blood samples for transfusion compatibility testing.
How Blood Collection Tubes Work
When blood is drawn, it is placed into a collection tube that may contain additives. These additives either allow the blood to clot (as in the red-top tube) or prevent clotting (as in the green, lavender, and blue-top tubes). The tubes are then processed by centrifugation, which separates the blood into different components like plasma, serum, and blood cells.
Need More Information? We’re Here to Help!
At Honey T Scientific Ltd., we’re committed to providing the best support for your testing needs. If you have any questions about our test tubes, require assistance with your order, or need more details, don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
